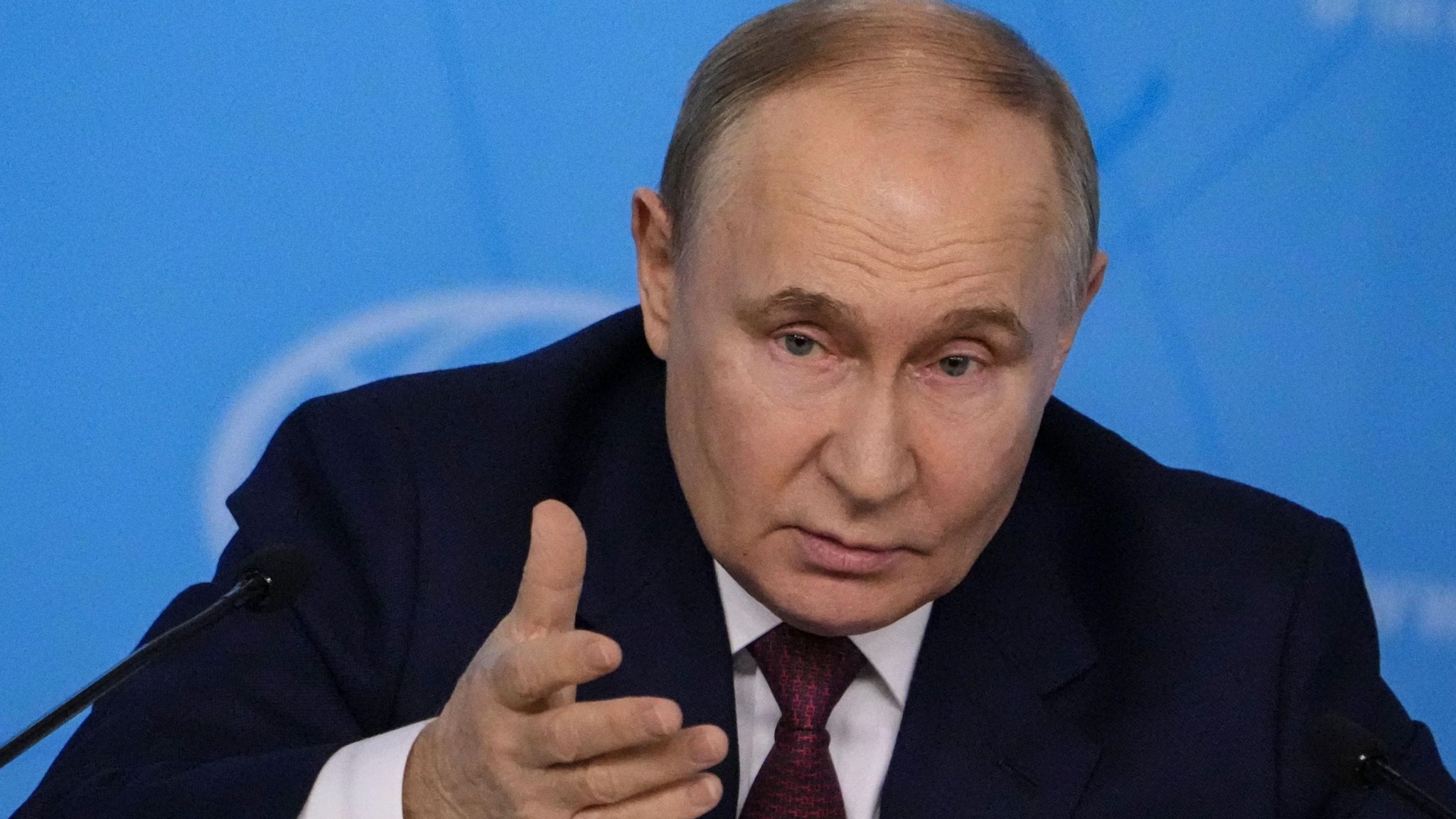
Vladimir Putin, the current President of Russia, is one of the most influential and controversial figures in contemporary global politics. His leadership has significantly shaped Russia’s domestic policies and its stance on the international stage. This article delves into Putin’s early life, political career, leadership style, major policies, and his impact on both Russia and the world.
Vladimir Putin Early Life and Career

Vladimir Putin was born on October 7, 1952, in Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg), Russia. He grew up in a communal apartment, typical of Soviet-era housing, and his early life was marked by the hardships of post-World War II Soviet Union. Putin developed an interest in sports, particularly judo, which he pursued vigorously, earning a black belt and several championships.
Education and KGB Career
Vladimir Putin graduated from Leningrad State University in 1975 with a degree in law. His academic background laid the foundation for his analytical and strategic approach to politics. Upon graduation, he joined the KGB, the Soviet Union’s security agency, where he served as an intelligence officer for 16 years. His KGB career included a stint in Dresden, East Germany, where he was stationed from 1985 to 1990. This period honed his skills in intelligence, surveillance, and clandestine operations, which would later influence his political strategies.
Entry into Politics
Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Putin returned to Leningrad and worked in the mayor’s office as an advisor on international affairs. He quickly ascended the political ladder, demonstrating a knack for governance and strategic planning.
Rise to Power
In 1996, Vladimir Putin moved to Moscow and joined President Boris Yeltsin’s administration. His rapid rise continued as he held various key positions, including Director of the Federal Security Service (FSB) and Secretary of the Security Council. In 1999, Yeltsin appointed Putin as Prime Minister. Later that year, Yeltsin resigned, and Putin became Acting President. His decisive handling of the Second Chechen War and his promise to restore order and stability earned him widespread popularity. He won the presidential election in 2000, marking the beginning of his long tenure in Russian politics.
Presidential Terms
First Two Terms (2000-2008)
Putin’s first two terms as President were characterized by efforts to consolidate power, stabilize the economy, and restore Russia’s global influence. He implemented various reforms to strengthen the central government and curtail the influence of oligarchs. Economic growth during this period was bolstered by rising oil prices, leading to increased living standards and a resurgence of national pride.
Prime Minister (2008-2012)
Due to constitutional term limits, Putin could not run for a third consecutive term in 2008. Instead, he endorsed Dmitry Medvedev as his successor and assumed the role of Prime Minister. During this period, Putin maintained significant influence over Russian politics, guiding major decisions and policies.
Return to Presidency (2012-Present)
In 2012, Vladimir Putin returned to the presidency amid allegations of electoral fraud and widespread protests. Despite the controversy, he won the election and has since been re-elected, most recently in 2018. His current term is set to end in 2024, but constitutional amendments passed in 2020 could allow him to remain in power until 2036.
Leadership Style and Policies

Authoritarian Governance
Putin’s leadership style is often described as authoritarian. He has centralized power, curtailed political freedoms, and suppressed dissent. The state controls major media outlets, and political opponents face significant obstacles, including imprisonment and exile. Critics argue that Putin’s governance undermines democratic principles, but his supporters claim that it ensures stability and order.
Economic Policies
Economically, Putin has focused on energy exports, particularly oil and natural gas, to drive growth. His administration has implemented policies to attract foreign investment, modernize infrastructure, and reduce dependency on Western financial systems. However, economic sanctions imposed by the West following the annexation of Crimea in 2014 have challenged these efforts, leading to economic stagnation and increased self-reliance.
Foreign Policy
Putin’s foreign policy aims to reassert Russia’s influence on the global stage. Key elements include strengthening ties with China, expanding military capabilities, and countering Western influence. The annexation of Crimea, involvement in the Syrian Civil War, and alleged interference in foreign elections reflect his strategic vision of a multipolar world where Russia plays a leading role.
Major Achievements and Controversies
Crimea and Ukraine
The annexation of Crimea in 2014 remains one of the most significant and controversial actions of Putin’s presidency. While it boosted his popularity domestically, it led to international condemnation and sanctions. The conflict in eastern Ukraine, where Russia is accused of supporting separatist movements, continues to strain relations with the West.
Syrian Civil War
In 2015, Russia intervened in the Syrian Civil War to support President Bashar al-Assad’s regime. The military campaign helped Assad regain control over significant territories and demonstrated Russia’s ability to project power latoto login beyond its borders. Critics argue that the intervention exacerbated the humanitarian crisis, but it cemented Russia’s role as a key player in Middle Eastern geopolitics.
Domestic Repression
Domestically, Vladimir Putin administration has been criticized for human rights abuses and the suppression of political dissent. High-profile cases, such as the imprisonment of opposition leader Alexei Navalny and the crackdown on protests, highlight the regime’s intolerance of opposition. International organizations frequently condemn Russia for these actions, calling for greater respect for human rights and democratic principles.
Personal Life and Public Image

Cult of Personality
Vladimir Putin public image is carefully crafted to project strength, decisiveness, and patriotism. State media often portrays him engaging in various activities, from playing ice hockey to riding horses shirtless, reinforcing his image as a vigorous and capable leader. This carefully managed persona appeals to many Russians who value stability and national pride.
Personal Life
Vladimir Putin personal life is shrouded in secrecy. He was married to Lyudmila Shkrebneva for 30 years before their divorce in 2013. They have two daughters, Maria and Katerina, who maintain low profiles. Despite various rumors and allegations about his personal relationships and wealth, Putin remains enigmatic about his private affairs.
Legacy and Future
Enduring Influence
Vladimir Putin’s influence on Russia and global politics is undeniable. He has reshaped Russia’s political landscape, restored a sense of national pride, and positioned the country as a formidable global power. His legacy, however, is marked by controversies, including human rights abuses, electoral interference, and aggressive foreign policies.
Future Prospects
As Putin’s current term nears its end, speculation about his future continues. The constitutional amendments allowing him to extend his rule suggest that he may seek to remain in power, ensuring continuity of his policies. However, internal and external challenges, such as economic pressures, social unrest, and international tensions, will shape the next phase of his leadership.
Conclusion Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Putin’s journey from a modest upbringing in Leningrad to the helm of Russian politics is a testament to his strategic acumen and resilience. His tenure has transformed Russia, for better or worse, and his actions continue to reverberate globally. As a leader, Putin embodies both the strengths and flaws of modern Russia, making him a pivotal figure in understanding the country’s past, present, and future.
Read More Article About “Vada Pav: The Iconic Street Food of Mumbai 2024“