Table of Contents
ToggleIn the aviation community, the terms MiG-41 and Russia’s 6th generation fighter project are omnipresent with many opinions, speculations, and expectations. Designed to succeed the legendary MiG-31, the aircraft is projected to revolutionize the concept of air superiority and provide the Russian Air Force with the latest technologies. Named PAK-DP, the PAK-DP, the MiG-41, as it is known to the western audience, will be a distinct innovation in the world of military aviation with its stealth technology, supersonic speed, and powerful armament.
This article is a comprehensive analysis of the MiG-41 project, covering its background, design, technology profile, and strategic perspective. We will also compare it with modern 5th “and 6th” generation aircraft presented by other countries to understand its place in the context of the modern air warfare landscape.
Background and Historical Context
The MiG-41 project is a mere continuation of Russia’s interception planes initiative. Developed during the Cold War to intercept American bombers and cruise missiles, the aircraft has served its purpose dutifully following its commissioning into service in 1981. The interceptor has accomplished its mission by accomplishing what no ordinary fighter aircraft can achieve, flying at supersonic speeds and intercepting high-altitude targets due to its radar and long range missiles.
However, the times have changed, and the threats facing modern Russia cover hypersonic missiles, UAVs, and stealth aircraft. Aware of this new challenge, the Russian air force launched the 6th Generation interceptor project to retire its aging MiG-31, and MiG-41 was born in 2014. The wdbos login MiG-41 is intended to secure air dominance over the US and other potential adversaries fighter planes and outsmart hypersonic missiles, stealth planes, and low-Earth orbit satellites while enhancing its operational range through speed and fuel consumption. This would render the interceptor advanced and distinct from its predecessor MiG-31.

Design and Development in MiG-41
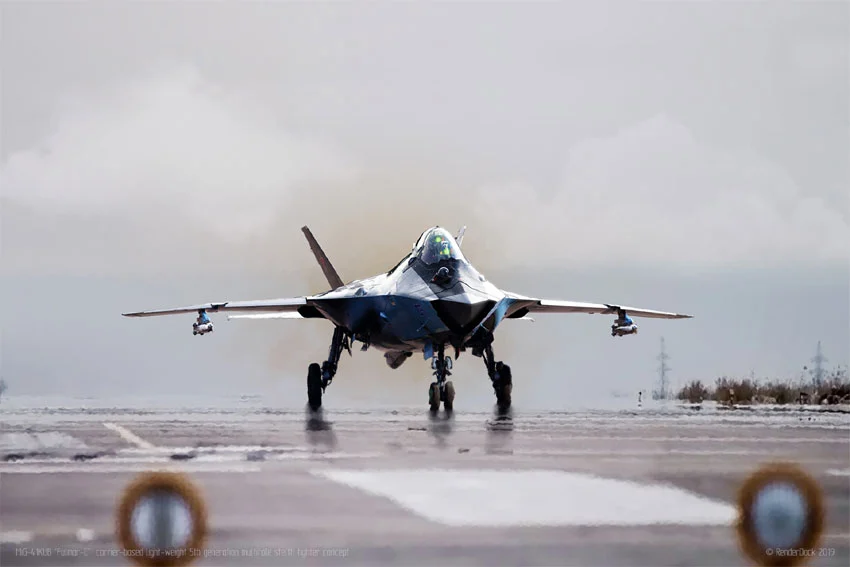
Due to the forbidden character of the MiG-41 program, as neither detailed specifications nor designs are to be disclosed to the public, its exterior, design, and characteristics can be inferred only from experts’ assessments and leaked information. One of the hallmarks of the 6th generation is stealth, and it is likely that the MiG-41 is designed with this quality in mind. First, it is intended to have a RCS close to 0: the concept implies reducing it through various methods. These include angular shaping, using radar-absorbent materials, reducing infrared signature via more efficient engines and the cooling system, and improved aerodynamics by making the general design sleek and eliminating all possible protrusions.
I think that the aircraft will exhibit a delta-wing configuration with twin vertical stabilizers that allow it to be fast and agile at once. It is also possible that the MiG-41 will have a variable-geometry wing that it can switch between high-speed without much drag and low-speed, allowing maneuvers thanks to available surfaces. Another feature that will make the MiG-41 so efficient is its engines.
Most sources believe that the 6th generation aircraft will be powered by new jet engines – ground-effect engines – that are likely based on MiG-31 engines but upgraded. Their operating speed exceeds Mach 4, making them among the fastest fighters ever built.
They are also designed for high altitudes; the MiG-41 is supposed to operate at altitudes exceeding 20 km, which allows it to intercept high-flying targets. It is also going to have better fuel usage, as well as a more enhanced fuel management system, which will educate the overall flight range and endurance.
Advanced Avionics and Sensors
The MiG-41 will be equipped with cutting-edge avionics and sensor systems that will significantly improve its situational awareness and targeting capabilities. Among them is a new Active Electronically Scanned Array radar, an AESA, which will double the detection range and streamline the tracking of targets. An advanced Infrared Search and Track system capable of passive target detection will be extremely important when engaging low observable aircraft.
Furthermore, the MiG-41 will be fitted with next-generation Electronic Warfare systems to counter electronic emissions and gather information. It will be able to process data from multiple sensors into one single accurate image, a process similar to that of impactful source of data. The MiG-41 will be well-armed and will cover a wide range of targets. New long-range air-to-air missiles, such as the R-37M shot at enemy aircraft more than 300 km away and medium distance missile K-77M equipped with an active radar seeker, will be developed.
There may also be new hypersonic weapons capable of shooting down ballistic missiles and satellites. Sources suggest that the MiG-41 could be armed with direct energy weapons, such as lasers, to destroy oncoming missiles or drones. Additionally, the MiG-41 may have a command-and-control capability for Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles for reconnaissance and strike purposes.
Strategic Implications and Global Impact
The development of the MiG-41 is highly strategic for Russia; especially, its high speed and altitude capabilities will expand strategic depth for Russia, ensuring rapid response to threats across the vast Russian territory. Moreover, the ability to deploy the aircraft in the Arctic appears to be a particularly poignant statement, as the Arctic becomes one of the emerging geopolitical hotspots, given faster climate change and navigation opportunities. Also, the MiG-41’s capability to intercept hypersonic missiles is strategic in a way that it is responsive to emerging threats.
Hypersonic missiles, with the speed greater than Mach 5, are too fast to be detected using current radar systems and crucially difficult to intercept. The MiG-41 will allow Russia to equip the aircraft with hypersonic missiles and detection systems advanced enough to provide protection against such threats. On the other hand, the MiG-41 will not develop in a vacuum. The US and China are developing their 6th generation fighters as well. Specifically, the US NGAD Next Generation Air Dominance project is on the way, and it is going to be stealthy and AI-driven fighter.
The MiG-41 will compete with this fighter and will target F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II, America’s next-generation jet. China currently works on the J-20 and J-31 (both being 5th generation) fighters and is developing own 6th generation fighters. The MiG-41 will compete with the Chinese 6th planes in the Asian-Pacific region. Finally, two European 6th generation projects should be noted – UK’s Tempest and France-Germany-Spain’s Future Combat Air System.

Technological Challenges and Development Hurdles
Developing a 6th generation fighter jet is no mean feat, and making it accelerating such high speeds is even more demanding for the builders of the MiG-41. Creating an engine capable of propelling an aircraft to such great speeds while still proving to be efficient and reliable is not easy. The engine will require advanced materials and cooling systems to work as it would encounter extreme operating temperatures when accelerating past Mach 4.
On the other hand, maintaining a stealth configuration at such high speeds would also be difficult as surfaces would develop a lot of heat as a result of friction. Therefore, onboard materials would also need to be engineered to withstand such proved without interfering with their radar-absorbent properties. Additionally, maintaining or achieving the target radar cross-section and remaining aerodynamically viable would require sophisticated engineering.
Another challenging area will integration; while all of the best available avionics and sensor systems would be integrated into the MiG-41 platform, one must communicate with the other for targeted, precision situational awareness. The aircrafts radar, IRST, data fusion, and EW systems will have to work seamlessly, which requires advanced software and hardware development. Developing hypersonic weapons and directed energy platforms to work on the MiG-41 would also be a big challenge.
While hypersonic missiles must be able to carry enough power to be effective yet be compact enough to fit in the nimble fighter; the directed energy weapons would require significant miniaturization and optimization of portable power sources.
Comparison with Other 6th Generation Projects
The MiG-41 project is not the only 6th generation fighter jet under development. Other major military powers are also pursuing similar projects, each with its own unique characteristics.
Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) – United States
The U.S. is developing its NGAD fighter, which aims to replace the F-22 Raptor and complement the F-35. The NGAD is expected to feature:
- Stealth: Advanced stealth technologies to remain undetectable.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-assisted pilot support and autonomous drone coordination.
- Advanced Propulsion: Next-generation engines for higher speed and efficiency.
- Network-Centric Warfare: Integration with other military assets via secure data links.
Tempest – United Kingdom
The Tempest project, led by the UK, is a collaborative effort involving BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce, Leonardo, and MBDA. Key features include:
- Modular Design: Customizable airframe to meet different mission requirements.
- Swarm Drone Capability: Ability to control and deploy swarms of unmanned drones.
- Directed Energy Weapons: Potential integration of laser weaponry.
- Cyber Resilience: Enhanced cybersecurity measures.
Future Combat Air System (FCAS) – Europe
A joint project between France, Germany, and Spain, the FCAS aims to replace the Dassault Rafale and Eurofighter Typhoon. Key features include:
- Stealth and Supercruise: Advanced stealth with sustained supersonic cruising.
- Loyal Wingman: Integration with unmanned drones as force multipliers.
- Sensor Fusion: Comprehensive data integration for enhanced situational awareness.
Comparison Analysis
Each 6th generation project has its distinct focus areas, but they all emphasize stealth, advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and network-centric warfare. The MiG-41’s primary differentiators are its extreme speed and high-altitude capabilities, designed to counter hypersonic threats and intercept low-Earth orbit satellites. This makes it unique compared to Western and European counterparts, which focus more on modularity, drone coordination, and directed energy weapons.

Future Prospects and Conclusion
The MiG-41 project is still in its early stages, with the first flight expected sometime in the late 2020s. However, if the project meets its ambitious goals, it will establish a new benchmark in air superiority and interception capabilities. The MiG-41 will play a crucial role in securing Russia’s airspace, particularly in the Arctic region and along its vast borders. Its ability to counter emerging threats like hypersonic missiles and stealth aircraft will provide a significant strategic advantage.
Furthermore, the MiG-41 will influence the global arms race in 6th generation fighter jets, prompting other nations to accelerate their own projects. This competition will drive technological innovation in stealth, propulsion, and weaponry, ultimately reshaping the future of air combat.
In conclusion, the MiG-41 represents Russia’s bold vision for the future of air defense. While significant technological and logistical challenges remain, the project’s success could redefine the global balance of power in military aviation. With its blend of speed, stealth, and advanced weaponry, the MiG-41 embodies the cutting edge of 21st-century air warfare and will undoubtedly be a game-changer in the evolving landscape of military aviation.
If you enjoyed reading this article, please consider exploring our comprehensive analysis of CBSE, where we delve into the strategic evolution and modernization of regional military capabilities.