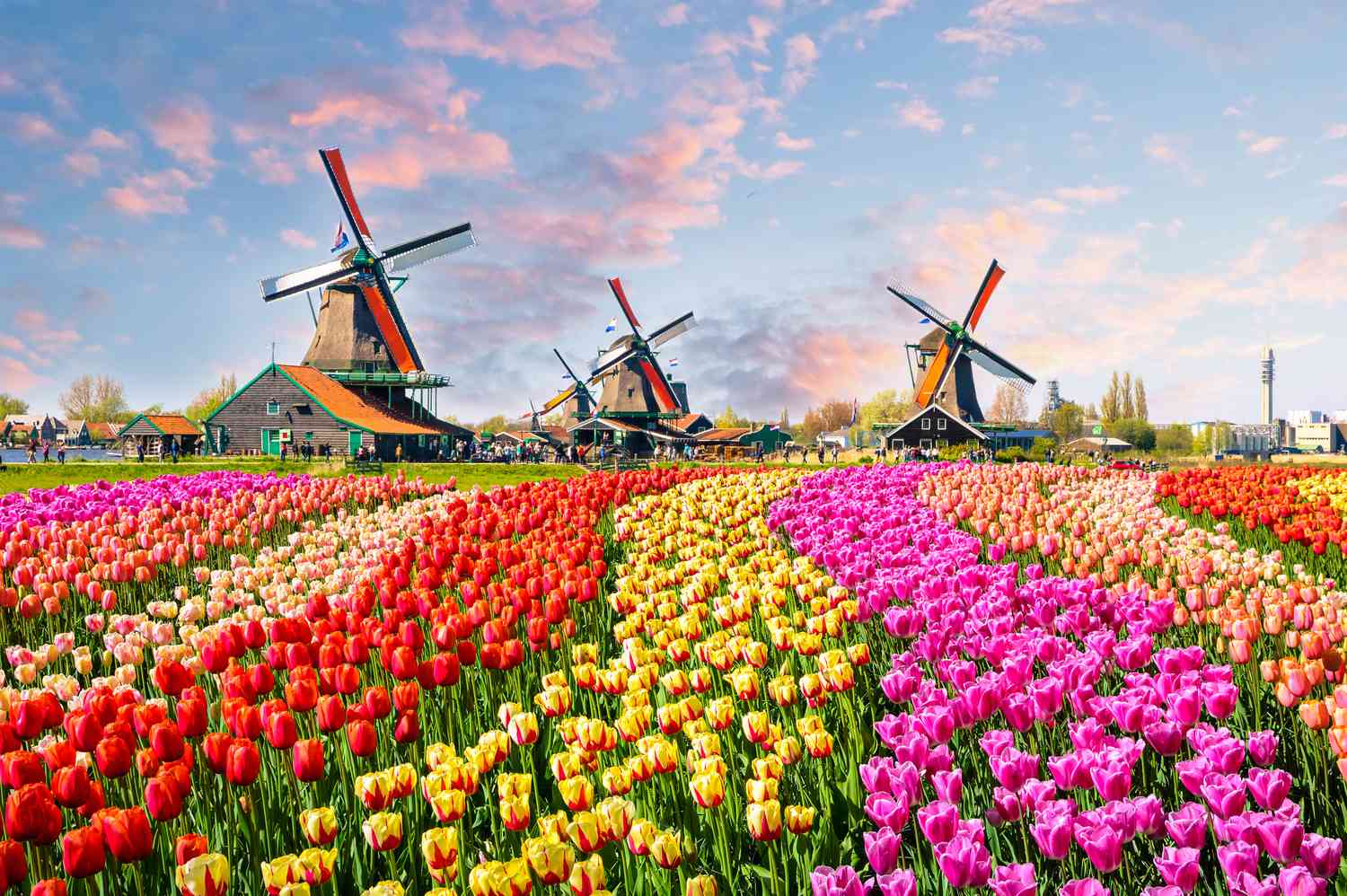
The Netherlands, often referred to as Holland, is a country located in Northwestern Europe. Known for its flat landscape, intricate canal systems, windmills, tulip fields, and progressive policies, the Netherlands is a nation that combines a rich history with a forward-thinking approach to modern challenges. This article explores the geography, history, culture, economy, and societal values of the Netherlands, highlighting what makes this country unique and influential on the global stage.
Geography and Climate The Netherlands
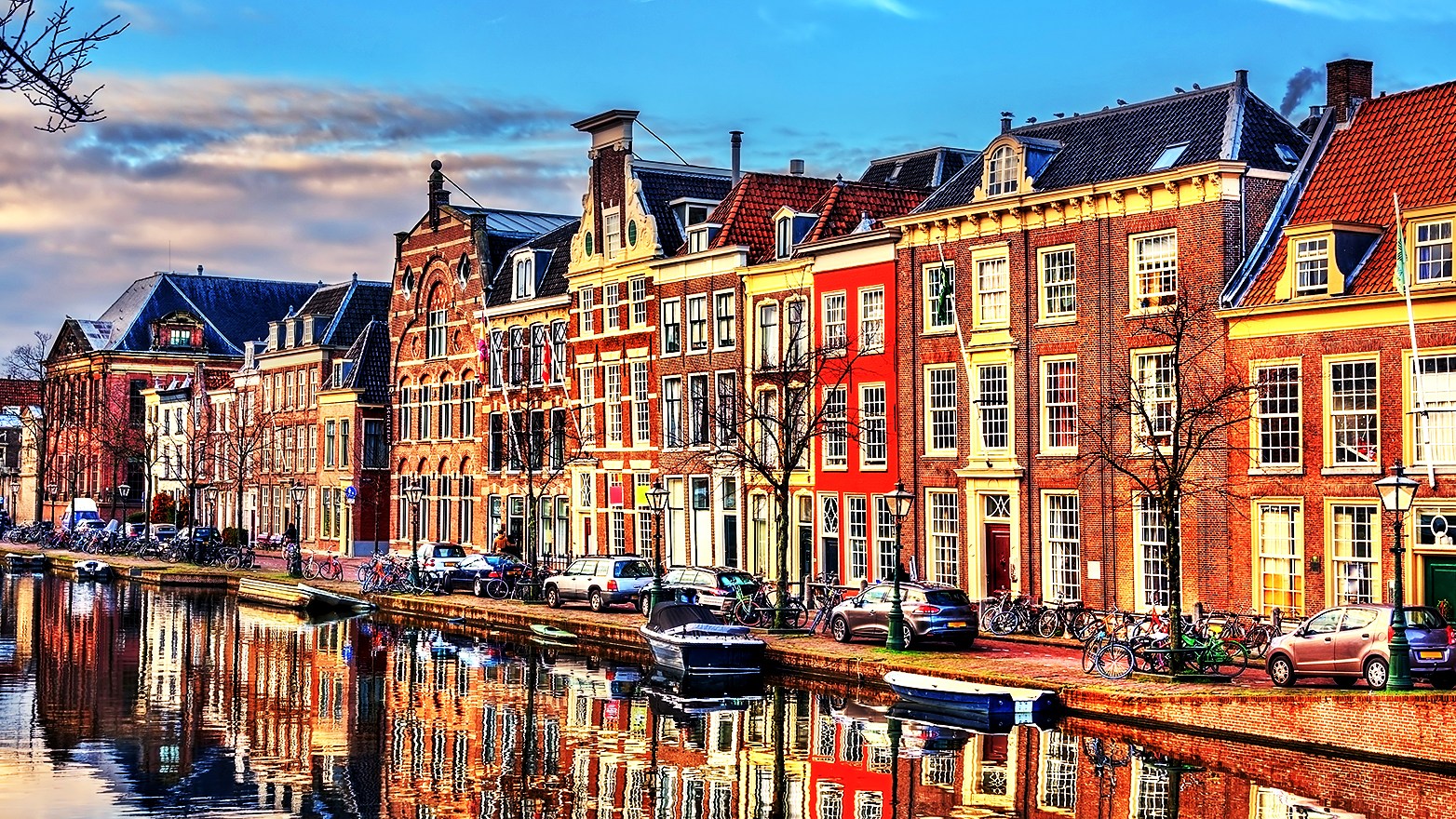

Location and Landscape
The Netherlands is bordered by Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest. The country covers an area of approximately 41,543 square kilometers, making it relatively small in size but densely populated. The landscape is predominantly flat, with about a quarter of its territory lying below sea level. This geographical feature has necessitated the creation of an extensive system of dikes, canals, and pumping stations to manage water levels and prevent flooding.
Major Cities
The Netherlands is home to several major cities, each with its own unique character and significance:
- Amsterdam: The capital city, known for its historic canals, vibrant cultural scene, and iconic landmarks such as the Anne Frank House and the Van Gogh Museum.
- Rotterdam: A major port city renowned for its modern architecture, innovative urban design, and the bustling Port of Rotterdam, one of the largest in the world.
- The Hague: The seat of the Dutch government and home to numerous international organizations, including the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court.
- Utrecht: A historic city with a medieval old town, famous for its Dom Tower and vibrant student population.
Climate
The Netherlands experiences a temperate maritime climate, characterized by mild winters, cool summers, and moderate rainfall throughout the year. The proximity to the North Sea influences the weather, bringing relatively stable temperatures and frequent precipitation. Despite the occasional storm, the climate is generally conducive to agriculture, which plays a significant role in the country’s economy.
History and Development
Early History
The history of the Netherlands dates back to prehistoric times, with evidence of human habitation as early as 250,000 years ago. During the Roman era, the region was inhabited by various Germanic tribes. In the Middle Ages, the area became part of the Holy Roman Empire, and by the 12th century, several city-states and principalities emerged, leading to a period of economic and cultural growth.
The Dutch Golden Age
The 17th century, known as the Dutch Golden Age, was a period of unprecedented prosperity and cultural flourishing. The Netherlands established itself as a major maritime power, with the Dutch East India Company (VOC) playing a pivotal role in global trade. During this time, Dutch art, science, and philosophy thrived, producing renowned figures such as Rembrandt, Vermeer, and Spinoza.
Modern History
The 19th and 20th centuries saw the Netherlands transition into a modern, industrialized nation. Despite suffering significant damage during World War II, the country rapidly rebuilt and became a founding member of key international organizations, including the United Nations, NATO, and the European Union. The post-war period was marked by economic growth, social progress, and the development of a comprehensive welfare state.
Culture and Society

Language and Religion
The official language of the Netherlands is Dutch, while Frisian is also recognized as an official language in the province of Friesland. English is widely spoken, and many Dutch people are multilingual, reflecting the country’s international outlook.
Religion in the Netherlands is diverse, with Christianity (both Protestantism and Catholicism) being the largest religious affiliation. However, secularism is prevalent, and a significant portion of the population identifies as non-religious. The country is known for its religious tolerance and freedom of belief.
Arts and Literature
The Netherlands has a rich cultural heritage, particularly in the fields of art and literature. The Dutch Golden Age produced some of the world’s most famous artists, including Rembrandt van Rijn and Johannes Vermeer. Dutch literature also boasts notable figures such as Anne Frank, whose diary has become one of the most widely read books in the world.
The country continues to be a vibrant center for contemporary art, with numerous galleries, museums, and cultural institutions showcasing both historical and modern works. Events like the International Film Festival Rotterdam and Amsterdam’s International Documentary Film Festival attract global audiences.
Festivals and Traditions
Dutch culture is marked by a variety of festivals and traditions. Some of the most notable include:
- King’s Day (Koningsdag): Celebrated on April 27th, this national holiday honors the birthday of King Willem-Alexander with street markets, concerts, and parties across the country.
- Sinterklaas: A traditional festivity held on December 5th, where children receive gifts from Sinterklaas (Saint Nicholas) and his helpers.
- Carnival: Particularly popular in the southern provinces, this pre-Lenten festival features parades, costumes, and revelry.
Cuisine
Dutch cuisine is characterized by hearty, simple dishes that make use of local ingredients. Some traditional foods include:
- Stroopwafels: Thin waffle cookies filled with caramel syrup.
- Haring: Raw herring served with onions and pickles, typically eaten as a snack.
- Bitterballen: Deep-fried meatballs often served as a bar snack.
- Cheese: The Netherlands is famous for its cheeses, including Gouda, Edam, and Leyden.
Economy and Innovation

Economic Structure
The Netherlands has a highly developed, open economy with a strong emphasis on international trade. Key sectors include:
- Agriculture: The Netherlands is one of the world’s largest exporters of agricultural products, thanks to its advanced farming techniques and innovation.
- Technology and Innovation: The country is a leader in technology, particularly in areas such as water management, renewable energy, and high-tech industries.
- Finance: Amsterdam is a major financial center, hosting numerous multinational corporations and financial institutions.
Innovation and Sustainability
The Netherlands is known for its innovative approaches to sustainability and environmental management. The country has pioneered techniques in water management, including the construction of dikes, polders, and advanced gengtoto flood control systems. Dutch companies and research institutions are also at the forefront of developing renewable energy technologies, circular economy practices, and sustainable agriculture.
Transportation and Infrastructure
The Netherlands boasts an extensive and efficient transportation network, including:
- Bicycling: The country is renowned for its bicycle-friendly infrastructure, with dedicated bike lanes and parking facilities.
- Public Transportation: An extensive network of trains, buses, and trams provides reliable and convenient travel options.
- Ports and Airports: The Port of Rotterdam is one of the busiest in the world, and Amsterdam Schiphol Airport is a major international hub.
Social Values and Progressive Policies
Social Equality
The Netherlands is known for its progressive social policies and commitment to equality. The country has a comprehensive welfare system that provides healthcare, education, and social security to its citizens. Gender equality is strongly emphasized, and the Netherlands consistently ranks high in global gender equality indices.
LGBTQ+ Rights
The Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage in 2001. The country is widely recognized for its LGBTQ+ rights and acceptance, offering comprehensive protections against discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.
Environmental Awareness
Environmental sustainability is a core value in Dutch society. The country has ambitious goals for reducing carbon emissions, increasing renewable energy production, and promoting sustainable urban development. Initiatives such as the Delta Works flood protection system and the Greenports program for sustainable agriculture exemplify the Netherlands’ commitment to environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
The Netherlands is a dynamic and forward-thinking country that combines a rich cultural heritage with a commitment to innovation and sustainability. From its picturesque landscapes and historic cities to its progressive social values and economic prowess, the Netherlands offers a unique blend of tradition and modernity. As the country continues to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its influence on global culture, economy, and environmental practices remains significant. Whether exploring its vibrant cities, experiencing its cultural festivals, or learning from its innovative approaches, the Netherlands stands as a beacon of progress and resilience.
Read More Article About “Jun SEVENTEEN: A Multifaceted Talent in K-Pop 2024“