Electrical safety is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe environment in homes, workplaces, and public spaces. Electricity, while essential for modern living, poses significant hazards if not managed properly. Electrical accidents can result in severe injuries, fires, and even fatalities. This article explores the importance of electrical safety, common electrical hazards, preventive measures, and best practices for ensuring electrical safety in various settings.
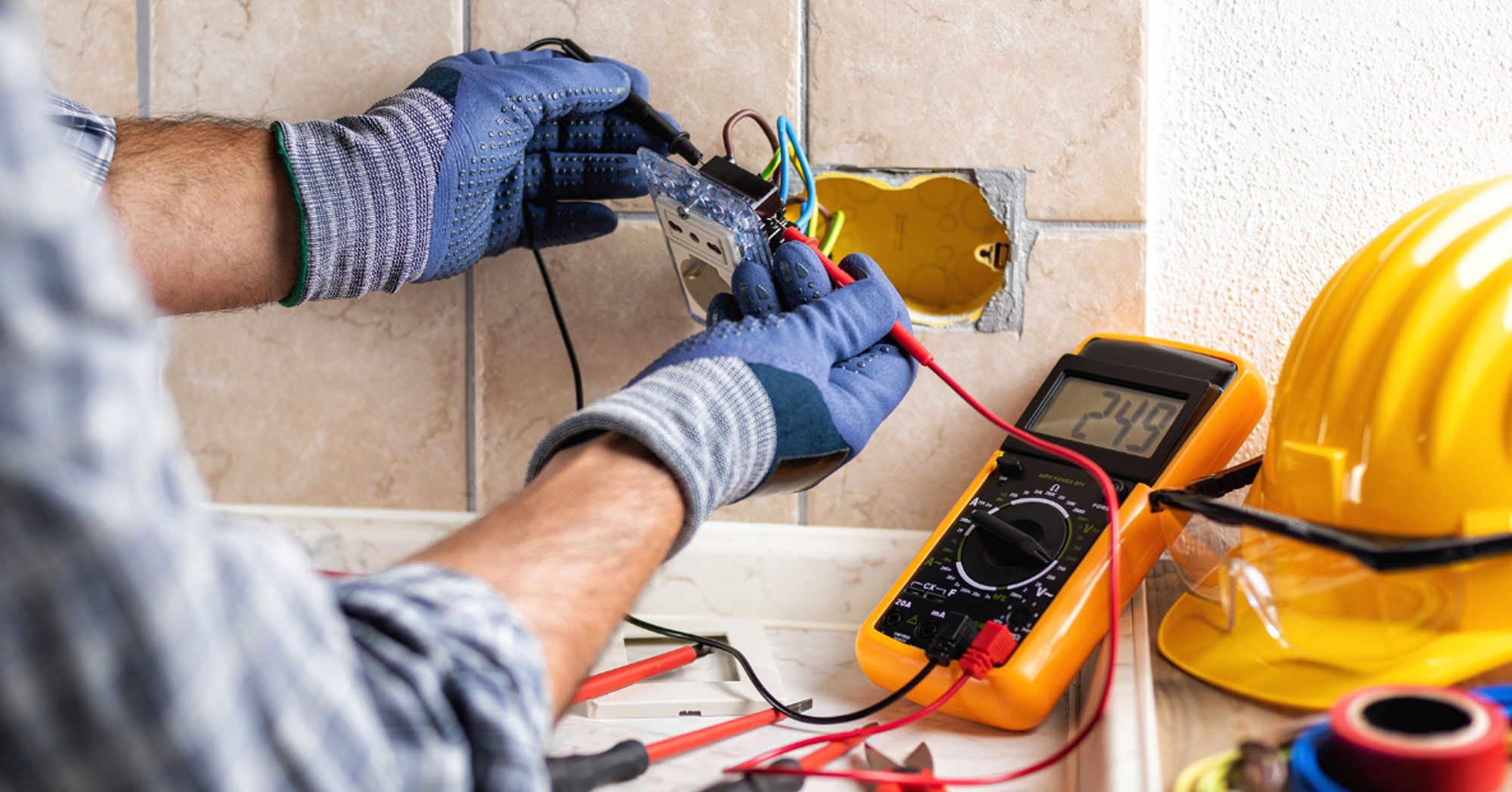

The Importance of Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is paramount because electricity, while highly beneficial, can be incredibly dangerous. Understanding and implementing proper safety measures can prevent accidents and save lives. Here are key reasons why electrical safety is important:
- Preventing Injuries and Fatalities: Electrical accidents can cause serious injuries such as burns, shocks, and electrocution. In severe cases, they can be fatal. Ensuring electrical safety helps protect individuals from these risks.
- Avoiding Property Damage: Electrical fires can cause significant property damage, leading to costly repairs and replacements. Proper safety measures can prevent such incidents.
- Ensuring Compliance: Adhering to electrical safety standards and regulations is mandatory in many regions. Compliance ensures legal and insurance requirements are met and reduces the risk of penalties.
- Promoting Productivity: In workplaces, electrical safety helps maintain a safe working environment, which can enhance productivity and reduce downtime caused by electrical accidents.
Common Electrical Hazards
Understanding common electrical hazards is the first step toward preventing them. Here are some of the most prevalent electrical hazards:
- Overloaded Circuits: Plugging too many devices into a single outlet or circuit can cause overheating, leading to fires.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged, frayed, or improperly installed wiring increases the risk of electrical shocks and fires.
- Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, so using electrical devices near water sources can result in electrocution or short circuits.
- Improper Use of Extension Cords: Overusing extension cords, or using them for permanent wiring solutions, can lead to overheating and fires.
- Defective Appliances: Appliances with damaged cords, plugs, or internal components can cause shocks and fires.
- Lack of Grounding: Electrical systems and devices that are not properly grounded increase the risk of electrical shock.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents. Here are essential steps to enhance electrical safety:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of electrical systems and appliances to identify and address potential hazards. Look for signs of wear and tear, such as frayed wires or discolored outlets.
- Qualified Electricians: Always hire qualified electricians for installation, maintenance, and repair work. DIY electrical work can be dangerous and is often against regulations.
- Proper Wiring: Ensure that wiring is up to code and capable of handling the electrical load. Use appropriate wiring materials and techniques to prevent overheating and short circuits.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): Install GFCIs in areas where electricity and water are likely to meet, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. GFCIs can detect imbalances in electrical currents and shut off power to prevent shocks.
- Surge Protectors: Use surge protectors to safeguard electronic devices from power surges that can cause damage and increase the risk of fire.
- Proper Use of Extension Cords: Use extension cords only as temporary solutions and avoid overloading them. Ensure they are in good condition and rated for the intended use.
- Avoid Water Exposure: Keep electrical devices and outlets away from water sources. Use waterproof covers for outdoor outlets and ensure hands are dry before handling electrical devices.
- Labeling and Signage: Clearly label circuit breakers and electrical panels. Use signage to indicate high-voltage areas and remind individuals of electrical safety practices.
Best Practices for Electrical Safety
Adopting best practices for electrical safety luna togel can further reduce risks and promote a safe environment. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Education and Training: Educate and train individuals on electrical safety practices. This includes recognizing hazards, using equipment correctly, and knowing how to respond in emergencies.
- Childproofing: In homes with children, use childproof outlets or outlet covers to prevent accidental contact with electrical sources.
- Unplugging Unused Devices: Unplug devices that are not in use to prevent overheating and reduce energy consumption.
- Correct Use of Appliances: Follow manufacturer instructions for all electrical appliances. Do not modify plugs or use appliances for unintended purposes.
- Routine Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for electrical systems and appliances to ensure they remain in good working condition.
- Emergency Preparedness: Have a plan in place for electrical emergencies. Ensure that fire extinguishers suitable for electrical fires are readily available and that individuals know how to use them.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): In workplaces, provide appropriate PPE for employees who work with or near electrical systems. This includes insulated gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing.
Responding to Electrical Emergencies
Knowing how to respond to electrical emergencies can prevent injuries and minimize damage. Here are some steps to take in the event of an electrical emergency:

- Electrical Shock: If someone receives an electrical shock, do not touch them directly. Turn off the power source if possible, or use a non-conductive object to move them away from the source. Call emergency services immediately and administer first aid if necessary.
- Electrical Fire: For electrical fires, do not use water to extinguish the flames. Use a Class C fire extinguisher or a fire blanket. If the fire is small and contained, turn off the power source if it is safe to do so. Evacuate the area and call the fire department.
- Power Outage: During a power outage, turn off and unplug non-essential electrical devices to prevent damage when power is restored. Use flashlights instead of candles to avoid fire hazards.
- Circuit Breaker Trips: If a circuit breaker trips, it indicates an overload or short circuit. Identify and address the cause before resetting the breaker. If the problem persists, contact a qualified electrician.
Conclusion
Electrical safety is a vital aspect of maintaining a safe environment in homes, workplaces, and public spaces. By understanding common electrical hazards and implementing preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure a safer living and working environment. Regular inspections, proper use of electrical devices, and adherence to safety standards are essential components of electrical safety. By staying informed and proactive, we can protect ourselves and others from the dangers associated with electricity.
Read More Article About “Chawanmushi: The Art of Japanese Steamed Egg Custard“



























